Introduction to Play
Play is an Appspace extension that allows you to create Play channels that provide simple IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) experiences with live broadcast TV channels, and on-demand content. Play utilizes data streaming to distribute these live and on-demand media in full broadcast quality over a data network to multiple devices with multiple Spaces, offering high levels of picture quality, flexibility, and scalability.
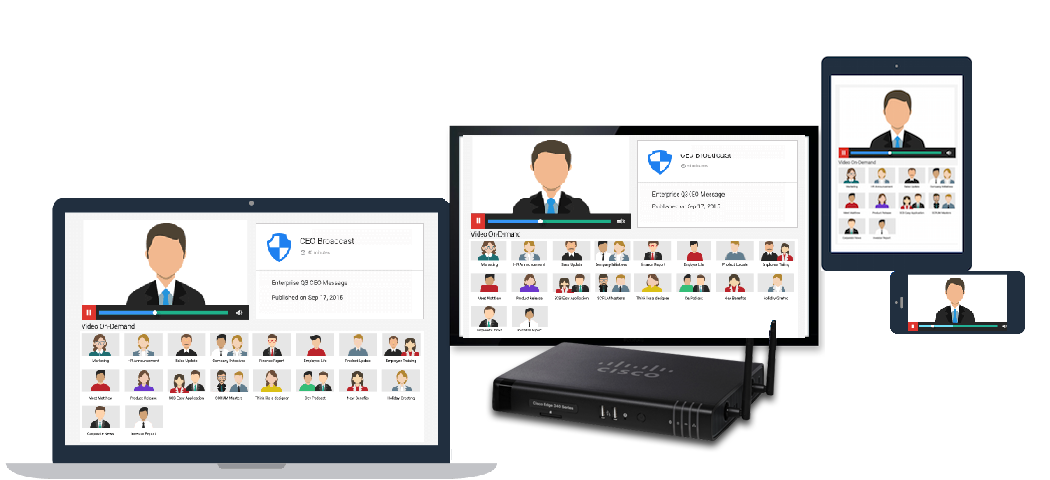
You can choose to experience Play via:
- Appspace App-driven devices. Click here for a list of Supported Devices.
- Web Clients (web browsers) on web-enabled devices such as desktop computers, smartphones, and tablets.
- Cisco Edge 340 digital media players.
The Play extension uses Spaces as a mechanism to allocate multiple content, Live TV Channels, devices, users, and user groups, to each Space. Live TV Channels, are live video feeds encoded and delivered as IP streams associated with EPG (Electronic Program Guides) data, while on-demand content are images and videos added directly from folders within the Appspace Library.
When you add new content to a folder that is already allocated to a Space, the newly added content automatically appears in the related Space and is delivered to all devices in the Space. Similarly, when a device is added to a device group that is already allocated to a Space, the device is automatically added to the Space.
All Play data are network specific. Therefore, you can only view and allocate content, users, and devices, that are within the network assigned to you. Similarly, you can share content from a Web Client, however, to view the shared content, one must have access to the Space the content belongs to.
Access and IDs in Play
Once you allocate devices and users to a particular Space, each user or device is allocated one Appspace ID for authentication in Play, which consumes one ID from the central pool of Appspace IDs. Appspace IDs are unique identifiers used by Appspace to track users and devices, which replaces the formerly used Client Access License (CALs) provided in your subscription.
The below describes how users or devices access a Space and how Appspace IDs are consumed during authentication:
Registered Device
Devices registered in Play are given access to an assigned Space without the need to input user credentials. Each device is given one Device ID and consumes one Appspace ID.
Authenticated User
Users must input an Appspace registered user credentials in a Web Client (web browser) to view the Spaces allocated to the user, user group, or network. Each user credential used to access a Space consumes one Appspace ID.
Note
Currently, to view IPTV videos in any mode in Play, you must be connected to the network, however, Appspace is working on making this available offline in the coming releases.
IPTV broadcast in Play
IPTV broadcasts primarily use multicast protocols for live streaming. However, Play supports the HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) protocol with chunked download to conform to webcast guidelines that use the unicast HTTP protocol for web-enabled devices. All Appspace App-driven devices, browsers, and the Cisco Edge 340 digital media player, support the HLS protocol.
By optimizing HLS, Play is able to provide high quality viewing experience that is adaptable to any kind of network over WiFi, 3G, or NAT (Network Address Translation) connections. Video streams are downloaded in small fragments, preventing packet loss, high bandwidth usage, and latency. HLS is also efficiently optimized by proxy servers, resulting in increased uptime. Based on your device and network bandwidth, you can choose to stream High Definition (HD) videos seamlessly in Play.
Note
As HLS is a unicast protocol, it would be beneficial to have a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to deliver video fragments seamlessly.
Apart from the HLS protocol, devices such as BrightSign and Cisco Edge 340 also support the MPEG2-TS UDP Multicast stream with either the MPEG-2 or the H.264 codecs, a bandwidth-conserving mechanism that reduces data network traffic by simultaneously delivering a single stream of information to thousands of recipients.
Note
If your current network uses a multicast protocol, you have a range of options to convert your multicast streams to HLS, which include free or paid software from vendors such as Cisco, or you may choose to optimize your network by allowing media player devices to use the multicast protocol while web based devices and browsers can use the HLS protocol.